
Abstract
Is ginseng good for male enlargement? Sure, Asians have used this type of ginseng for centuries to boost stamina, sex drive, and erection quality, and published research in the Journal of Urology confirms its efficacy as a treatment for erectile dysfunction.
Ginseng Clinical Study Results
Research has shown that ginseng may be a useful alternative for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It seems that compounds in it may protect against oxidative stress in blood vessels and tissues in the penis and help restore normal function. Additionally, studies have shown that ginseng may promote the production of nitric oxide, a compound that improves muscle relaxation in the penis and increases blood circulation.
First Study
Aim
To examine the treatment efficacy of Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) in impotent men with erectile dysfunction (ED)
Methods
A total of 60 patients presenting mild or mild to moderate ED were enrolled in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in which the efficacies of KRG and a placebo were compared. The patients received either 1,000 mg (3 times daily) of KRG or a placebo.
Results
The five-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) score after the treatment was significantly higher in the KRG group compared with that before the treatment (from 16.4 +/- 2.9 to 21.0 +/- 6.3, P < 0.0001). In contrast, there was no difference before and after the treatment in the placebo group (from 17.0 +/- 3.1 to 17.7 +/- 5.6, P > 0.05). In the KRG group, 20 patients (66.6%), reported improved erection, significant in the global efficacy question (P < 0.01); in the placebo group there was no significance. Scores on questions 2 (rigidity), 3 (penetration), 4, and 5 (maintenance), were significantly higher for KRG than those for the placebo when those questions were answered after 12 weeks of each treatment (P < 0.01). When the score in the KRG group was compared to the placebo group after the treatment, there was a significant improvement in total score (IIEF-5 score) in questions 3 and 5 for the KRG-treated group (P < 0.001 and P < 0.0001, respectively). The levels of serum testosterone, prolactin, and cholesterol after the treatment were not statistically significant differences between the KRG and the placebo group (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Our data show that KRG can be an effective alternative to the invasive approaches for treating male ED.
Second Stuty
Abstract
Several reports have promoted the root-derived Korean red ginseng (KRG; Panax ginseng) as an alternative treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED), and ginsenosides are known to be the principal active ingredients of ginseng. Recent studies showed that ginseng berries produce more ginsenosides than KRG; thus, we investigated the ability of the Korean ginseng berry extract GB0710 to relax the penile corpus cavernosum smooth muscle (CCSM) in this study. As a comparative control, the results were compared to those obtained using KRG. In addition, possible mechanisms of action for GB0710 were investigated. While KRG and GB0710 both displayed dose-dependent relaxation effects on precontracted rabbit CCSM in vitro, GB0710 was shown to be more potent than KRG. The GB0710-induced relaxation could be partially reduced by removing the endothelium. In addition, pre-treatment with several nitric oxides (NO) inhibitors significantly inhibited the relaxation of muscle strips. Furthermore, administration of GB0710 increased intracavernosal pressure (ICP) in a rat in vivo model in both a dose- and duration-dependent manner. Intracellular NO production in human microvascular endothelial cells could be induced by GB0710 and inhibited by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine. In conclusion, GB0710 had a greater relaxation effect on rabbit CCSM than did KRG extract, and increased ICP in a rat model in both a dose- and a duration-dependent manner. This relaxing effect might be mediated by NO production.
Introduction
One of the etiological causes of ED is the reduced bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO). This causes insufficient relaxation of smooth muscle in the penile corpus cavernosum, leading to a subsequently insufficient inflow of blood. Several extensive studies have investigated the positive effects of ginseng on ED, thereby implicating the NO pathway as the mechanism of action. Among these, various reports have promoted the root-derived Korean red ginseng (KRG; Panax ginseng) as an alternative treatment for ED, citing the stimulatory effect of KRG on the corpus cavernosum smooth muscle (CCSM) of the penis. The principal active ingredients of ginseng are ginsenosides (also called ginseng saponins), which are amphiphilic molecules comprised of an aglycon backbone (a hydrophobic four-ring steroid-like structure) linked to hydrophilic carbohydrate side chains that consist of monomers, dimers, and tetramers.
Materials and methods
Preparation of GB extract (GB0710)
Raw GB (Panax ginseng, CA, Meyer) were harvested in July from plants cultivated in the Chungbuk province in Korea, and the seeds were separated and removed. The flesh, juice, and skin of the GB were dried in hot air. The dried GB were first refluxed with 70% ethanol for 10 h, after which the extract was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure at 45 °C, thus obtaining the GB extract (GB0710).
Preparation of red ginseng extract (ginseng root)
Red ginseng (Panax ginseng, CA, Meyer), cultivated and manufactured in Chungbuk province in Korea was added to ethanol and extracted under reflux. The extract was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The concentrations of seven major ginsenosides in GB0710 and KRG extract were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The results are shown in:
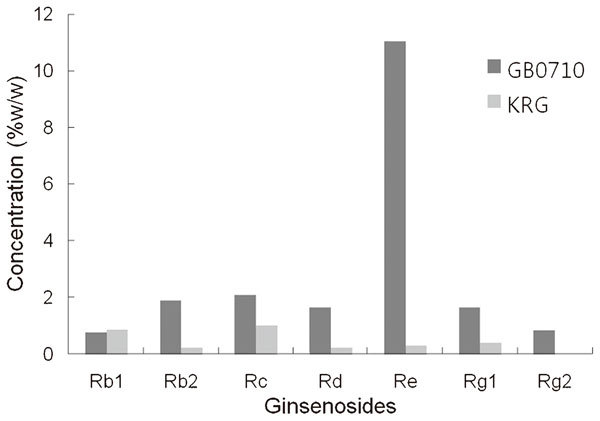
Results
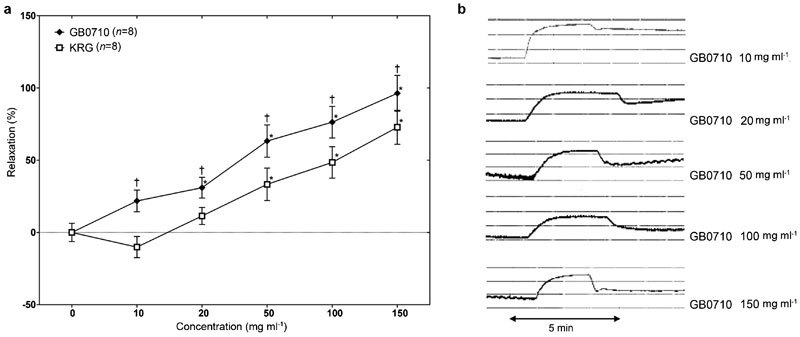
In vitro comparison of GB0710 with KRG extract with regard to the relaxation of isolated rabbit CCSM
While the KRG extract caused contraction at low concentrations in the Phe-induced precontracted CCSM, both GB0710 and KRG extract caused relaxation of the CCSM at high concentrations (≥10 mg ml−1 for GB0710, and ≥20 mg ml−1 for KRG). Hence, GB0710 showed a more powerful relaxation effect than KRG extract. For both substances, a concentration-dependent relaxation effect was observed, with the maximal effect at 150 mg ml−1 (96.3%±12.4% in GB0710, and 72.8%±11.8% in KRG) (Figure 2). The half-maximal inhibitory concentration of GB0710 was 39.3 mg ml−1, and that of KRG was 111.9 mg ml−1.
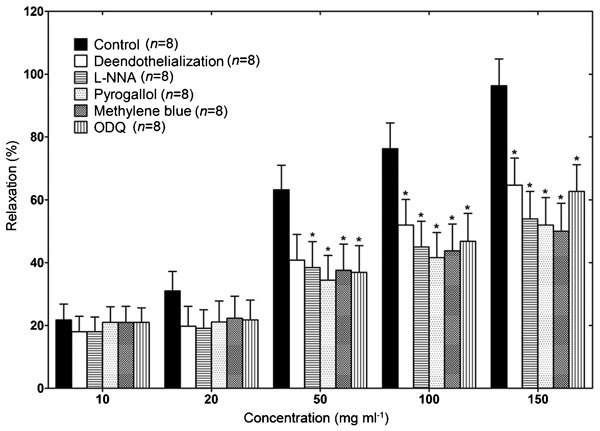
GB0710-induced CCSM relaxation in conjunction with the NO pathway
This GB0710-induced relaxation was partially reduced by removing the endothelium (P<0.05; ). In addition, pre-treatment with any of the NO-inhibitors was able to partially inhibit the relaxation of muscle strips (P<0.05; ).
Third Study
Ginseng is often referred to as the King of all herbs and is found to be a promising agent to improve general well-being. Ginseng has also been reputed as an aphrodisiac and is used to treat sexual dysfunction as well as to enhance sexual behavior in traditional Chinese medical practices. Data from animal studies have shown a positive correlation among ginseng, libido, and copulatory performances, and these effects have been confirmed in case-control studies in humans. In addition, ginseng is found to improve the sperm quality and count of healthy individuals as well as patients with treatment-related infertility. These actions are mostly attributed to ginsenosides, the major pharmacological active components of ginseng. This review compiles the current knowledge about the multifaceted effects of ginseng on male reproductive function, and also focuses on its mechanisms of action that may represent novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of male reproductive diseases or disorders.
Introduction
Infertility is a growing problem in the world. In 2010, an estimated 48.5 million couples worldwide were infertile. In approximately 40% of these couples, the male partner has been either the sole or a contributing cause of infertility. Herbal therapy is increasingly popular worldwide as a way to treat infertility. In the United States, 17% constantly visited herbal therapists in the past 18 mo out of the 29% of infertile couples who use complementary and alternative medicine. In a clinic-based survey conducted in Jordan, 44% of infertile patients use herbal medicine as part of their infertility treatment. Among them, 8% went for Chinese medication. In South Australia, 29% of interviewed infertile subjects use herbal remedies, in which 4.2% uses ginseng.
Ginseng is one of the most precious herbs in traditional Chinese medicine. There are at least nine species of ginseng and are mostly named by their geographical origins, such as Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng), American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium), and Japanese ginseng (Panax japonicus). The genus name “Panax” is given to ginseng by the Russian botanist Carl A Meyer in 1843. “Panax” means “all-healing” in Greek, and Panax ginseng is conventionally referred to the Asian ginseng. Ginseng has been reported to have diverse physiological effects in multiple systems, including cardiovascular, immune, and neuronal. It has also been used to enhance sex performance and satisfaction. In this review, we will summarize the effects of ginseng on male sex performance and spermatogenesis. Recent evidence on its mechanisms of action that may represent novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of male reproductive diseases or disorders will be discussed.
Sex Performance
Ginseng is commonly taken by itself or with an herbal formula to enhance sexual performance in traditional Chinese medical practices. The beneficial effects have been scientifically evaluated and confirmed in meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials. For example, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 45 men with moderate to severe erectile dysfunction had found improvement in their scores on erectile performance and sexual satisfaction after treated with three times daily doses of 900 mg Korean red ginseng for 8 wk.A similar study on 60 men with erectile dysfunction also reported marked improvement in erectile function including rigidity, penetration, and maintenance of erection after taking Korean red ginseng (1000 mg) three times daily for 12 wk.
In animal studies, treatment with Korean red ginseng and ginseng berry extract has been shown to significantly relax the pre-contracted penile corpus cavernosum smooth muscles of rabbits in vitro, and increase the intracavernosal pressure of rats in vivo. Data from studies on ginseng berry extract suggest that this action is nitric oxide (NO) dependent. The pharmacologically active components of ginseng, ginsenosides, are known to be able to induce NO synthesis in endothelial cells and perivascular nerves and to augment vascular smooth muscle cell’s sensitivity to NO. This release of NO causes smooth muscle to relax, thus allowing more blood to enter the erectile bodies known as corpus cavernosum and causing erection. Among the ginsenosides, Rg1 has been found for NO production in endothelial cells by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-dependent, non-genomic mechanisms, and administration of Rg1 (10 mg/kg) significantly enhances NO release and cyclic GMP (cGMP) accumulation in corpus cavernosum of mice.
Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Ginseng is a vital constituent of traditional Chinese medicine and has been used to treat various physical conditions for thousands of years, importantly as an aphrodisiac and is used to treat sexual dysfunction as well as to enhance sexual behavior and gonadal functions. Therefore, the use of ginseng appears to be important for the development of novel therapeutics or to increase the effectiveness of the current treatment strategies for male reproductive diseases or disorders. However, its molecular mechanisms of action remain elusive. Research in this area should be carried further. A versatile assay for high-throughput expression profiling will prove useful to reveal the molecular functions of different ginsenosides and how the different signal networks are orchestrated. Further evaluations are also needed to validate some of the medicinal benefits using modern analytical tools and technology-based analyses. Different approaches to synthesize and/or modify natural ginsenosides can also be considered to increase the efficacy/potency, metabolic stability, and oral bioavailability for clinical applications.
Suggest the bet gensing cream for you, SHOP NOW